- Azoxystrobin
- Bitertanol
- Captan
- Carboxin
- Carbendazim
- Cymoxanil
- Cuprous Oxide
- Copper Hydroxide
- Cyproconazole
- Cyprodinil
- Dimethomorph
- Diniconazole
- Difenoconazole
- Epoxiconazole
- Fluazinam
- Fludioxonil
- Fosetyl-aluminium
- Hexaconazole
- Imazalil
- Iprodione
- Kasugamycin
- Mancozeb
- Metalaxyl
- Metalaxyl-M
- Penconazole
- Propiconazole
- Prochloraz
- Propineb
- Pyraclostrobin
- Thiophanate-methyl
- Tebuconazole
- Tetraconazole
- Tricyclazole
- Triadimenol
- Triadimefon
- Tridemorph
- Trifloxystrobin
Difenoconazole
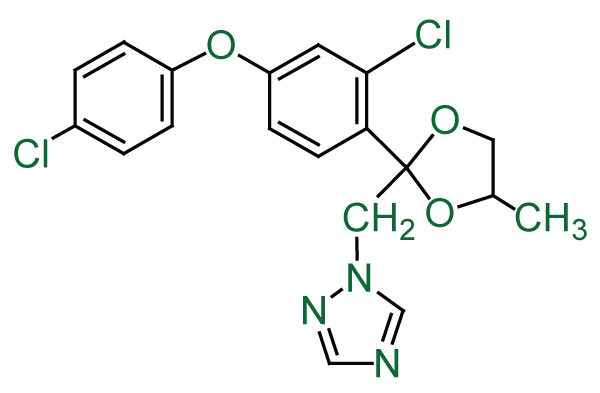 other name: 1-[2-[2-chloro-4-(4-chlorophenoxy)phenyl]-4-methyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole
other name: 1-[2-[2-chloro-4-(4-chlorophenoxy)phenyl]-4-methyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole
CAS No.: [119446-68-3]
Molecular Formula: C19H17Cl2N3O3
Difenoconazole is a broad spectrum fungicide that controls a wide variety of fungi – including members of the Aschomycetes, Basidomycetes and Deuteromycetes families. It acts as a seed treatment, foliar spray and systemic fungicide. It is taken up through the surface of the infected plant and is translocated to all parts of the plant. It has a curative effect and a preventative effect. Difenoconazole can be applied to winter wheat, oilseed rape, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, broccoli/calabrese and cauliflower. It controls various fungi including Septoria tritici, Brown Rust, Light Leaf Spot, Leaf Spot, Pod Spot, Ring Spot and Stem canker. It also prevents Ear Discolouration in winter wheat. The mode of action of difenoconazole is that it is a sterol demethylation inhibitor which prevents the development of the fungus by inhibiting cell membrane ergosterol biosynthesis.
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Sterol demethylation inhibitor. Inhibits cell membrane ergosterol biosynthesis, stopping development of the fungus. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with preventive and curative action. Absorbed by the leaves, with acropetal and strong translaminar translocation. Uses Systemic fungicide with a novel broad-range activity protecting the yield and crop quality by foliar application or seed treatment. Provides long-lasting preventive and curative activity against Ascomycetes, Basidiomycetes and Deuteromycetes including Alternaria, Ascochyta, Cercospora, Cercosporidium, Colletotrichum, Guignardia, Mycosphaerella, Phoma, Ramularia, Rhizoctonia, Septoria, Uncinula, Venturia spp., Erysiphaceae, Uredinales and several seed-borne pathogens. Used against disease complexes in grapes, pome fruit, stone fruit, potatoes, sugar beet, oilseed rape, banana, cereals, rice, soya beans, ornamentals and various vegetable crops, at 30-125 g/ha. Used as a seed treatment against a range of pathogens in wheat and barley, at 3-24 g/100 kg seed. Phytotoxicity In wheat, early foliar applications at growth stages 29-42 might cause, in certain circumstances, chlorotic spotting of leaves, but this has no effect on yield. Formulation types DS; EC; FS; SC; WG.
