- Abamectin
- Acetamiprid
- Alpha-cypermethrin
- Amitraz
- Azamethiphos
- Bifenthrin
- Bacillus thuringiensis
- Carbosulfan
- Chlorfenapyr
- Chlorfluazuron
- Chlorpyfifos
- Clothianidin
- Cypermethrin
- Cyphenothrin
- Clofentezine
- Cyromazine
- Deltamethrin
- Diafenthiuron
- Diazinon
- Diflubenzuron
- Emamectin Benzoate
- Empenthrin
- Fipronil
- Flufenoxuron
- Fenazaquin
- Hexythiazox
- Hydramethylnon
- Imidacloprid
- Indoxacarb
- Lambda-cyhalothrin
- Lufenuron
- Malathion
- Methomyl
- Nitenpyram
- Novaluron
- Permethrin
- Propargite
- Profenofos
- Pymetrozine
- Pyriproxyfen
- Sulfluramid
- Teflubenzuron
- Tetramethrin
- Thiamethoxam
- Thiodicarb
- Trichlorfon
- Triflumuron
Amitraz
Other Name: N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-N-[[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)imino]methyl]-N-methylmethanimidamide
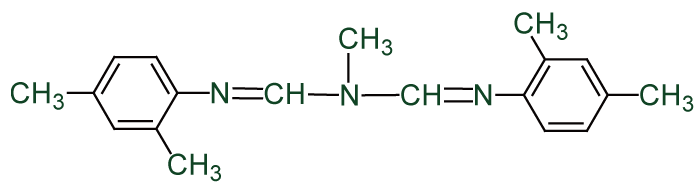 CAS Number: [33089-61-1]
CAS Number: [33089-61-1]
Molecular Formula: C19H23N3
Amitraz is a broad spectrum formamidine class acaricidal pesticide, normally it is recommended as an acaricide.
Amitraz has effects of contact-killing, apastia, repellent. it has certain effects such as stomach poisoning, fumigation and the suction effect.
Amitraz is effective against various instars of tetranychidae, but less effective against overwintering eggs. It has a variety of toxicity mechanisms with the main effect of inhibition of monoamine oxidase activity. It can stimulate non-cholinergic synapses of the central nervous system of pest mites. It can also effectively fight against pest mites which is resistant to other kinds of acaricide. Its efficacy can last for 40~50 days. It is mainly used for prevention and treatment of many kinds of pest mites among a variety of crops such as fruit, vegetables, tea, cotton, soybeans, and sugar beets. It also has good control effect against psyllid class and some kinds of lepidopteran pest’s egg. It also has partial control effects on scales, aphids and cotton bollworm, red bollworm, etc.  It can be further used for controlling cattle mites, sheep mites and bee mites. Mixing amitraz with organophosphate and pyrethroid, avermectin can enhance the effect and expand insecticidal spectrum.
It can be further used for controlling cattle mites, sheep mites and bee mites. Mixing amitraz with organophosphate and pyrethroid, avermectin can enhance the effect and expand insecticidal spectrum.
Amitraz is moderately toxicity to human, animal. Acute oral administration for rate: LD50 is 500~600 mg/kg; acute percutaneous administration of rabbit: LD50 > 200 mg/kg; acute inhalation for rat: LC50 of 65mg/L. It has low toxicity to bees, birds and other predators. It has irritant effects on human skin and mucous membrane and has inhibitory effect on the central nervous systems of human. No known specific antidote is available for treating poisoning. Toxicity to natural enemies: LC50 (mg/kg): Mallard 7000, Japanese quail 1800, the North American quail 788; LC50 (14 days) earthworm> 1000mg / kg; low toxicity to bees and predatory insects, LC50 (contacts)> 50μg / bee. Toxic to fish; The LC50 of 48 hours exposure to carp is 1.17 mg / liter. No accumulation in vivo toxicity.
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry
Mode of action
probably involves an interaction with octopamine receptors in the tick nervous system, causing an increase in nervous activity.
Mode of action
Non-systemic, with contact and respiratory action. Expellent action causes ticks to withdraw mouthparts rapidly and fall off the host animal.
Uses
Control of all stages of tetranychid and eriophyid mites, pear suckers, scale insects, mealybugs, whitefly, aphids, and eggs and first instar larvae of Lepidoptera on pome fruit, citrus fruit, cotton, stone fruit, bush fruit, strawberries, hops, cucurbits, aubergines, capsicums, tomatoes, ornamentals, and some other crops. Also used as an animal ectoparasiticide to control ticks, mites and lice on cattle, dogs, goats, pigs and sheep. Phytotoxicity At high temperatures, young capsicums and pears may be injured.
Formulation types EC; PO; WP.
