- 6-Benzylaminopurine(6-BA)
- Gibberellic Acid (GA3)
- 4-Indol-3-yibutyric Acid (IBA)
- Indol-3-yiacetic Acid (IAA)
- Forchlorfenuron (CPPU)
- 1-Naphthylacetic Acid (NNA)
- 2-(1-naphthyl)acetamide (NAD)
- Chlormequat chloride (CCC)
- Prohexadione-Calcium
- Thidiazuron (TDZ)
- Paclobutrazol
- Abscisic Acid (ABA)
- Brassinosteroid
6-Benzylaminopurine (6-BA)
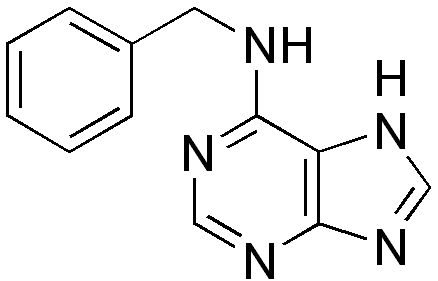
other name: [N-phenylmethyl-1H-purin-6-amine], [ 6-BA, 6-BAP, BAP, Benzyl Amino Purine, 6-Benzyladenine ]
CAS No.: [ 1214-39-7 ]
Molecular Formula: C12H11N5
6-Benzylaminopurine is known as plant growth regulators belong to family or classification of Cytokinins (also abbrev. as Kinin), Kinins are phytohormones which initiate cell division in tissues, including those whose cells do not divide in the absence of cytokinins even when optimally nourished and supplied with other phytohormones. Cytokinins occur in the endosperm of mazize and coconut, and in other plant organs.
True cytokinis were discovered as a result of efforts to find factors that would stimulate plant cells to divide. They were shown to affect many other physiological and developmental processes. These effects include the delay of senescence in detached organs, the mobilization of nutrients, chloroplast maturation, the expansion of cotyledons, and the control of morphogenesis. In the case of chloroplast maturation, delay of senescence, and mobilization of nutrients, cell division does not occur during the cytokinin induced response. In other words, cytokinins have a number of different, apparently unrelated rebulatory roles in higher plants.
A large number of chemical compounds have been synthesized and tested for cytokinin activity. Analysis of these compounds provides insight into structural requirements for activity. Nearly all compounds as active as cytokinins are 6-substituted aminopurines derivatives. 6-Benzylaminopurine (6-BA, BAP), which has found uses in agriculture, is an example of synthetic 6-substituted aminopurine cytokinin.
6-Benzylaminopurine has proven to accelerate plant cell growth and division and has recently developed as a color preserver in vegetables such as asparagus, broccoli, brussels sprouts, lettuce, and celery for extended color retention during harvesting, shipping and storage by using chlorophyll retention. 6-BA's success in increasing size and multiple budding characteristics in a variety of tropical and subtropical fruits and vegetables has attracted great interest in the agricultural economies. Two of N-6BAP's many attractions are its ability to display high activity in very diluted solution and its USFDA General Recognize as a Safe Status which requires no registration for its use.
Benefits of using 6-Bazylaminopurine (6-BA) are inlcuding:- Acceleration of cell division and the related DNA synthesis.
- Acceleration of inhibition of cell enlargement in leaves.
- Promotion of leaf bud formation and elimination of the related polarity, as well as the mutual inhibition of longitudinal growth.
- Promotion of root growth and root formation; occasionally inhibition.
- Influence of leaf shape and leaf pigments
- Promotion of germination
- Interruption of the rest period (dormancy)
- Increase in respiration and RNA and DNA synthesis.
- Inhibition of protein degradation, rejuvenation of the leaves
- Translocation of low-molecular nitrogen compounds but not inorganic ions.
- Increase size nad produce larger fruit
Our Technical Material (TC) have the specification as below:
| Items | Specification |
| Appearance | white crystalline powder |
| Content (by HPLC) | 98% min. |
| Loss on Drying | 0.5% max. |
| Residues after Ignition | 0.1% max. |
| Melt Point, °C | 267-235 |
GHS complaint Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for commercial product of 6-BA is available uopn requested.
